German Gotha GV Bomber
- World War I
- 1 min
By Crusader1307
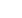
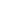
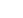
Considered the “first” strategic “night time” Bomber, it was developed for The Imperial German Air Corps late in the War (1917). Designed to carry twice as much fuel as a standard Fighter, they were constructed for distance and transporting a heavy bomb load. Previous versions of The Gotha-Class Bombers revealed their problematic large fuel nacelles (which would often rupture at altitude due to their placement to the engines). As a result, some 75% of The early Gotha Bombers were lost in combat. Smaller (and multiple nacelles) were installed inside the aircraft frame (away from possible heat sources). The Gotha GV Bomber was a “3 Seater” (Pilot and 2 Gunners). It had an operational ceiling of 21,000 feet. The Gotha had an 80 foot wingspan and was 41 feet long. It was capable of 88 miles per hour. The Gotha carried up to (14) 60-pound electrically activated bombs of various types. It also was armed with (3) 7.92mm Parabellum Model 14 Machine Guns.